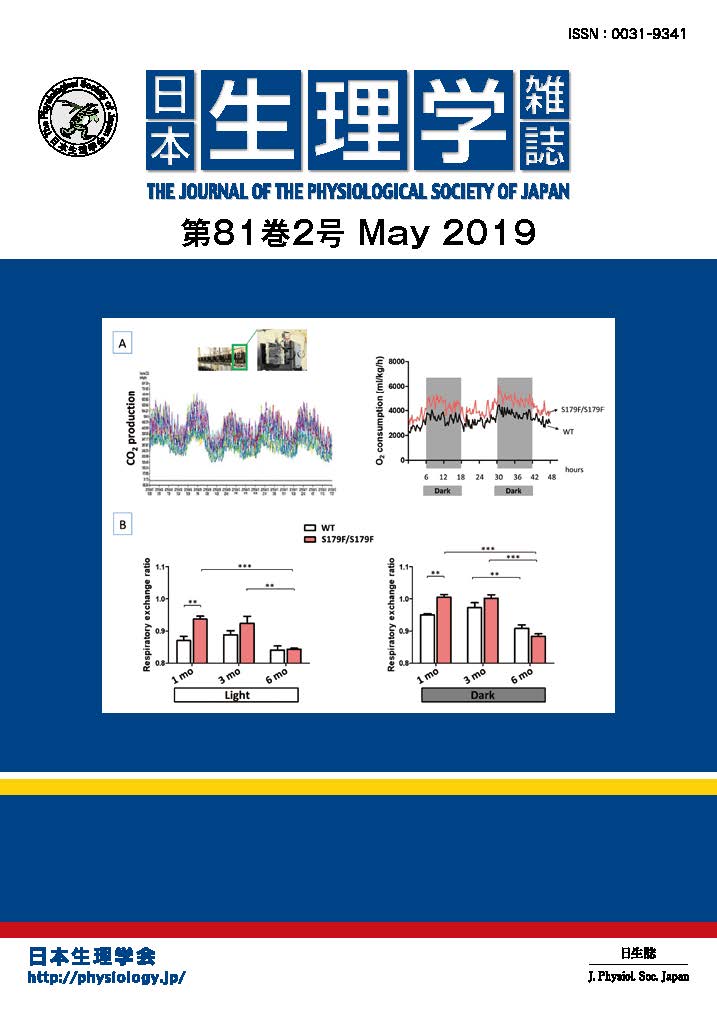
CONTENTS
- AFTERNOON TEA - 秋田天平 P.103~
- AFTERNOON TEA - 篠田陽 P.103~
- AFTERNOON TEA - 岡本士毅 P.103~
- INFORMATION - 成茂神経科学研究助成基金平成22 年度応募要領 P.108~
- INFORMATION - 東京大学大学院医学系研究科機能生物学専攻博士課程・修士課程入試説明会 P.108~
- INFORMATION - うま味研究会公開シンポジウム 「摂食機能と味覚・うま味の関連」 P.108~
- INFORMATION - 千里ライフサイエンスセミナー 「パーソナルゲノム時代の統合医療データベース戦略」 P.108~
- INFORMATION - 千里ライフサイエンス技術講習会第53 回 「ポストトランスクリプトーム時代の新たな戦略」 P.108~
- INFORMATION - 日本臨床体温研究会第25 回学術集会 P.108~
- INFORMATION - 信州大学医学部分子薬理学講座准教授公募 P.108~
- INFORMATION - Federation of Asia and Oceanian Physiological Society P.113~
- INFORMATION - 名古屋市立大学大学院・医学研究科 基礎医科学講座(細胞生理学分野)の教授公募 P.114~
- RECORDS - 「基礎医学教育・研究の活性化に対する要望書」を提出 P.115~
- CALENDAR - 主な研究集会日程 P.119~
- ABSTRACTS - 第42 回日本生理学会東北生理談話会 P.120~
- ABSTRACTS - 第61 回日本生理学会中国四国地方会 P.125~
表紙の説明
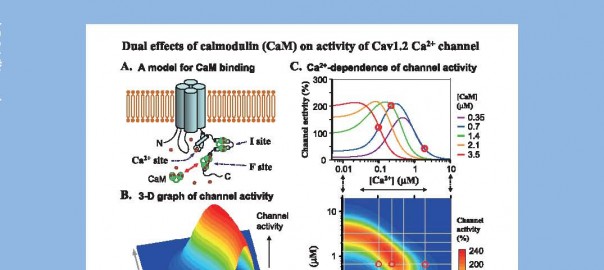
XXXVI International Congress of Physiological Sciences(IUPS2009)
(兼第86 回日本生理学会大会)
演題番号:P2AM-22-4 and 5
演題:“Multiple binding sites of calmodulin in the C-terminal tail of Cav1.2 Ca2+ channel. Facilitatory and inhibitory effects of calmodulin on activity of Cav1.2 Ca2+channel.”
演者:Hadhimulya Asmara1,韓冬雲1, 2, 3,蓑部悦子1, Zahangir A. Saud1,王午陽1,徐 建軍1,郝麗英1, 3,亀山正樹1
所属:1 鹿児島大・院医歯学総合研・神経筋生理,2 中国瀋陽薬科大学薬理,3中国医科大学薬学院薬理毒理学
Calmodulin (CaM) is thought to mediate the Ca2+-dependent facilitation (CDF) and inactivation (CDI) of Cav1.2 L-type Ca2+channel. However, a precise molecular mechanism is still unclear. In this study, we proposed a model for CaM- and Ca2+-mediated regulations of the channel (A), based on the experiments in the inside-out patches of isolated myocytes.
CaM (0.1-15 μM)+ATP (2.4-3 mM) induced channel activity with a bell-shaped concentrationactivity relationship at 10-2,000 μM [Ca2+]. The bell-shaped curve shifted to the left when [Ca2+] was increased, implying a possible molecular mechanism for CDF and CDI. A threedimensional representation of channel activity plotted against [CaM] and [Ca2+] revealed a complex feature of channel activity (B). The curves for channel activity as a function of [Ca2+] with fixed [CaM] (upper panel of C) are derived from the contour map of channel activity (lower panel of C), and reveal an initial increase and then a decrease of channel activity by increasing [Ca2+] (as exemplified by red circles). These results are consistent with the hypothesis that the Cav 1.2 channel has two CaM-binding sites (for facilitation and inactivation) and one additional Ca2+-sensing site within the channel.
氏名の「郝麗英」は,「はお(赤+阝,第3 水準1―92―70)りいん」と読みます.