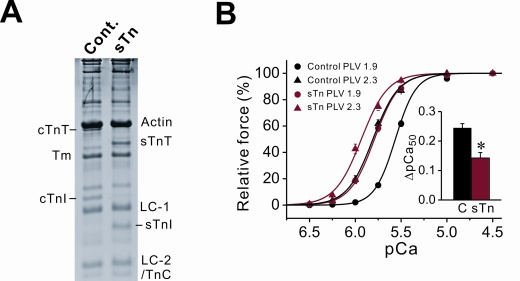
An increase in ventricular volume enhances the systolic performance of the heart; this is known as the Frank-Starling law of the heart. “The Law” is a manifestation of the sarcomere length dependence of myocardial activation, in which active force is a function of the resting sarcomere length (i.e., length-dependent activation). We have reported that passive force resulting from extension of the giant elastic protein titin (also known as connectin) operates as a triggering factor in this phenomenon. In the present study, we investigated whether or not length-dependent activation is modulated at the thin filament level. Quasi-complete reconstitution of thin filaments with rabbit fast skeletal troponin (sTn) attenuated length-dependent activation in porcine left ventricular muscle to a magnitude similar to that observed in rabbit fast skeletal muscle, accompanied by an increase in Ca2+ sensitivity of force (Fig. 1). We also found that sTn reconstitution accelerated cross-bridge kinetics at submaximal levels, suggesting that sTn reconstitution results in a decrease in the fraction of resting cross-bridges that can potentially produce active force. An increase in titin-based passive force, induced by manipulating the pre-history of stretch, enhanced length-dependent activation, with and without sTn reconstitution. These results favor the interpretation that troponin plays an important role in length-dependent activation via on-off switching of the thin filament state, in concert with titin-based regulation.
T. Terui, M. Sodnomtseren, D. Matsuba, J. Udaka, S. Ishiwata, I. Ohtsuki, S. Kurihara, and N. Fukuda. 2008. Troponin and Titin coordinately regulate length-dependent activation in skinned porcine ventricular muscle. J. Gen. Physiol. 131:275-283.
Figure 1. Effect of sTn reconstitution on length-dependent activation in porcine left ventricular muscle (PLV). (A) SDS-PAGE analysis. Cont., control PLV; sTn, sTn-reconstituted PLV. cTnT (sTnT), cardiac (skeletal) troponin T; cTnI (sTnI), cardiac (skeletal) troponin I; TnC, troponin C; Tm, tropomyosin; LC-1, myosin light chain 1; LC-2, myosin light chain 2. (B) Force-pCa curves in control (black lines) and sTn-reconstituted (red lines) PLV at SL 1.9 and 2.3 μm. Inset, ΔpCa50 (difference between the values of the mid-point (pCa50) of the force-pCa curve measured at SL 1.9 and 2.3 μm). C, control PLV. *P<0.05. Reproduced from The Journal of General Physiology, 2008, 131:275-283. Copyright 2008 The Rockefeller University Press.
*Department of Cell Physiology, The Jikei University School of Medicine, Tokyo, Japan